文章很多图源来自NTUSTISC例会视频,油管链接:NTUSTISC - Pwn 3 - YouTube
目前只支持到libc2.34版本
Heap-Based Buffer Overflow
最最基本的攻击方式,由于未对输入长度限制,且堆块是一片连续存储的内存空间特性。导致可以对其后高地址的chunk的各种信息进行覆写。

UAF(Use-after-free)
在free()掉chunk之后,原本指向chunk的指针由于程序猿自身的懒惰,没有将pointer = NULL; 导致依然可以使用该指针进行额外的操作
UAF漏洞一般常用于泄露,或者更改已经free掉的chunk中的信息,最常见便是libc的泄露,以及对Tcache/Fastbin链表的控制
当第一块chunk进入unsorted bin后,他的fd和bk指针会共同指向main_arena+88(具体偏移似乎会随着版本变化,做题时手动调试即可),意味着当存在UAF漏洞时,我们可以输出这个chunk的内容即能得到libc
Fastbin Dup
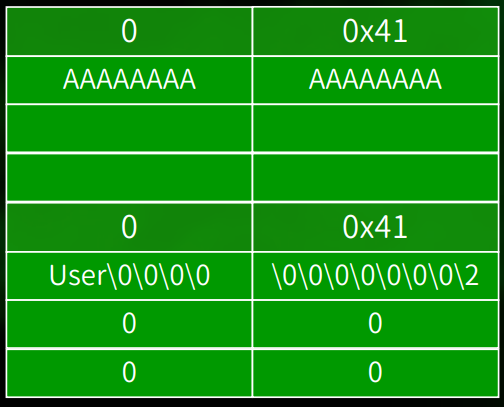
fastbin dup 实际是在fastbin链上实现的狭义的double free。由于fastbin 自身源码的缺陷,在对double free 的检测机制仅仅验证了当前free掉的chunk与fast bin 第一个chunk是否相同,而对于其他chunk则没有做检测。另外fastbin在free时会检测当前当前的chunk于头部chunk的size大小是否相同。
那么构造double free 时只需要穿插一块其他的chunk即可实现
1 | free(1); |
在完成double free 之后我们只需要malloc 这里的chunk1 就能得到一块 既是allocated 又是 free 状态的chunk。接下来我们就能对其fd指针进行修改,从而控制fastbin链表的方向是我们想要的地方,便能实现对任意地址的控制(读写)

额外需要注意的点:
- fastbin会对chunk头的大小进行检测,那么图中malice处chunk的size需要控制好
- libc2.26之后,free的小于0x410的chunk会先进入Tcache中,最多承纳7个chunk
- 且在tcache填满之后,malloc优先会取出tcache中的chunk,可以利用calloc不会申请tcache的特点
Tcache Dup
Tcache 在最近的几个libc中加入了多个机制,用于保证其安全性,这里我将分不同版本讨论
libc2.26-libc2.28
在这几个版本中,几乎没有检测机制,对同一块chunk直接进行double free即可,甚至比fastbin dup还要简易
libc2.29-libc2.31
在这几个版本中,tcache 的 bk指针处存放了一个8byte的随机数作为key,即代表这块chunk在tcache链中。每次free时,检测bk的位置的值是否为key,若是,则为doublefree。
绕过方式:存在UAF漏洞的情况下,我们可以直接更改,tcache中chunk的key值即可
libc2.32
Safe-linking(ptr xor)
libc2.32中引入了Safe-linking机制,应用于fastbin和tcache中
1 | static __always_inline void |
可以看到经glibc-2.32更新后,e->next不再是直接指向原来的tcache头指针,而是指向了经PROTECT_PTR处理过的指针,查看PROTECT_PTR定义:
1 |
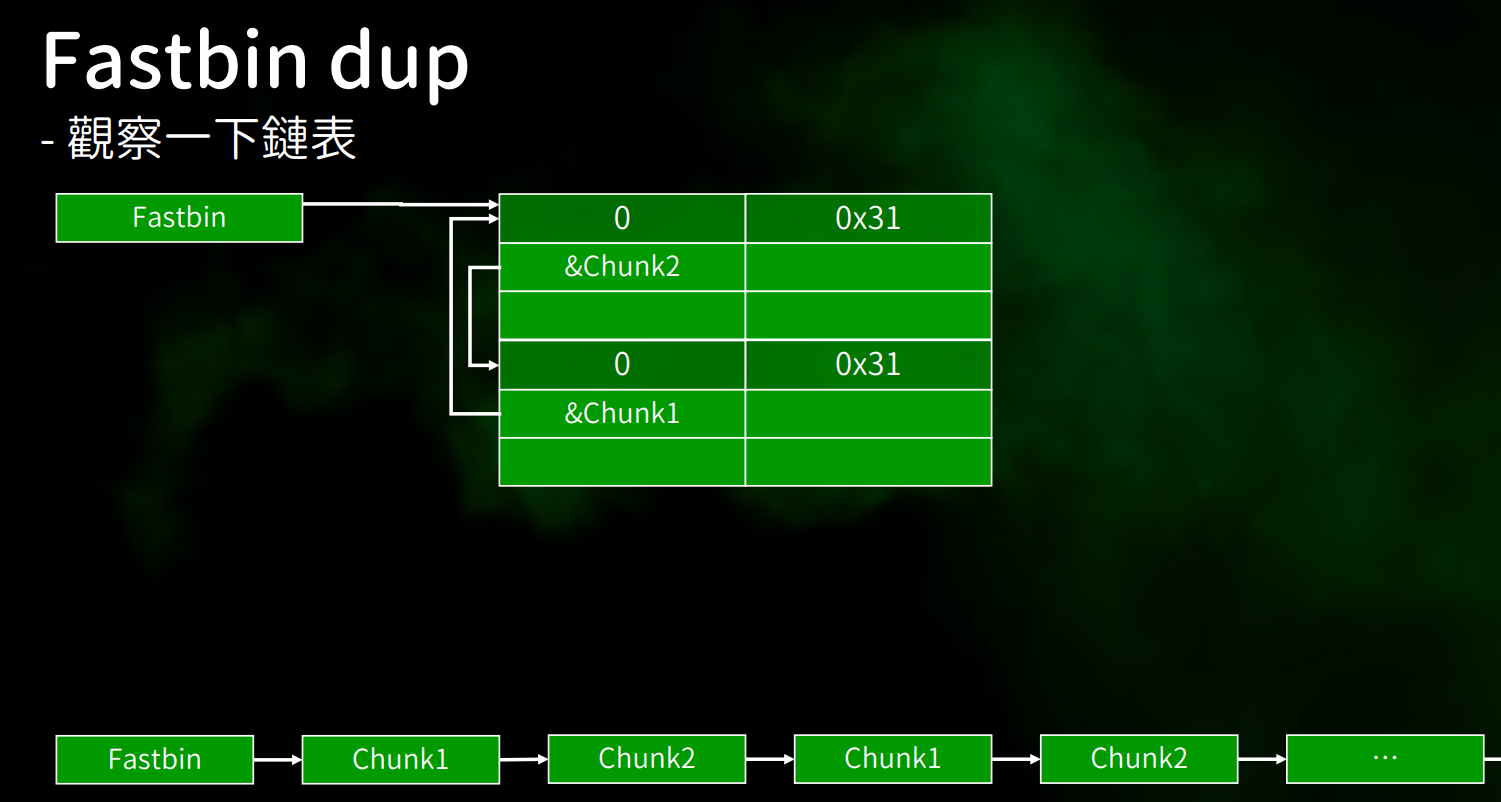
结合tcache_put()函数可以得出e->next最终指向了e->next地址右移12位后的值与当前tcache头指针值异或的结果,这里引用Safe-Linking设计师文章[1]中的一张图描述此过程:
其实就是一个简单的异或操作,这里所有的指针都进行了处理,具体细节可以自行查询,不过多赘述
内存对齐检测
此外,在glibc-2.32版本中还引入了对tcache和fastbins中申请及释放内存地址的对齐检测,以tcache_get()为例:
1 | static __always_inline void * |
aligned_OK()定义为:
1 |
可以看到内存地址需要以0x10字节对齐。
libc-2.34
glibc-2.34 的到来给予了hook劫持沉重的一击,移除了以下几个hook符号:
__free_hook
__malloc_hook
__realloc_hook
__memalign_hook
__after_morecore_hook
绕过思路
- 利用IO_vtable
- 利用exit_hook
- 劫持返回地址进行ROP
unsafe unlink
unsafe-unlink利用chunkfree时的合并机制,实现了地址的任意读写
使用条件:
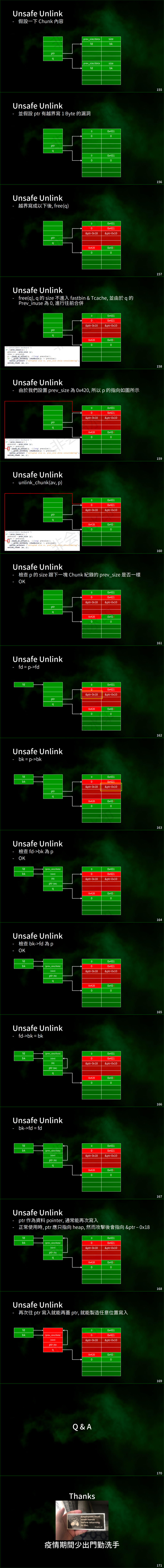
- 能够利用溢出或其他漏洞,将某chunk的size域的最低16进制位修改为0,例: 0x91 –> 0x90
1 | /*这是一段unsafe-unlink的示例代码,我们在最后成功利用这个漏洞, |
示例图